A motor is a device that turns electrical energy into motion. By creating a magnetic field with electricity, it causes the magnetic poles to push and pull, resulting in mechanical movement. Motors are crucial for generating mechanical motion, consuming 46% of the world’s yearly electricity production.
There are various types of motors, like BLDC motor, AC induction motor, servo motor, stepper motors, categorized by their principles or applications. They’re used extensively across different sectors, from everyday household gadgets to heavy-duty industrial machinery.

Motors are broadly divided into two categories: permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM motor) and AC induction motors.
These two types differ significantly in their structure, working principle, and their operational features.


Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM/BLDC motor)

Structure
A permanent magnet synchronous motor is a motor that uses permanent magnets to generate a magnetic field to achieve synchronous operation. Its rotor contains permanent magnets. The permanent magnets on the rotor are divided into surface permanent magnets (SPM) and internal permanent magnets (IPM) structures.

Working principle
The working principle of the permanent magnet synchronous motor is to drive the stator to input an alternating current to generate a magnetic field around the stator. The rotor is embedded with permanent magnets to generate a constant magnetic field without the need for external energy supply. The stator magnetic field is consistent with the permanent magnets. Magnetic fields interact to create rotational forces.


The PMSM motor requires a driver (motor controller) to form an alternating current and form an accurate magnetic field direction, so that the rotor operates at maximum torque. The driver can be designed separately from the motor, or it can be integrated with the motor to save space, facilitate installation, and reduce energy loss and interference.


Because DC can also be input to the driver, and the PMSM motor uses electronic commutation instead of carbon brush commutation, it is also called a brushless DC motor (BLDC motor).
PMSM motors are widely used in industrial drives, electric vehicles and other fields that require high energy efficiency and precise power control.
AC Induction Motor

Structure
An induction motor is a common type of AC motor that has no magnets in its rotor structure. The rotor consists of a cylindrical copper or aluminum conductor, that is placed in the rotor slots and connected by end rings, to form a closed loop.

Working principle
The working principle is based on electromagnetic induction: when alternating current is applied to the stator coil, it generates a rotating magnetic field, but this rotating magnetic field does not directly drive the rotor, but generates an induced current in the rotor conductor, which creates another magnetic field in the rotor, the interaction between these two magnetic fields causes the rotor to start spinning.

The closed conductors of the induction motor rotor are in the shape of a cage, so they are also called squirrel-cage motors. The rotors of some induction motors also have windings, which produce a stronger rotor magnetic field to suit larger torque starting requirements. This type of motor requires a slip ring and carbon brush structure to power the winding of the rotor, and the structure is more complex.
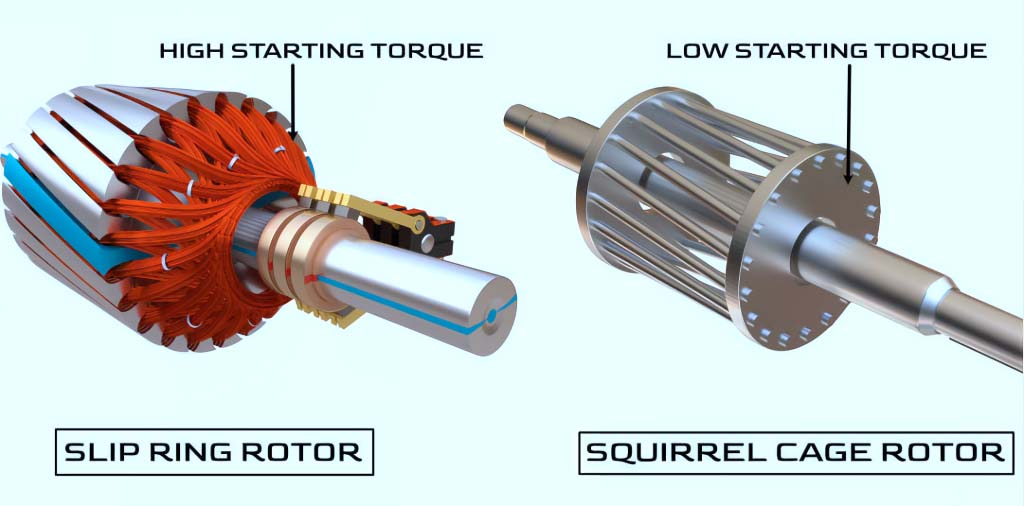
Since the rotor conductor needs to cut the stator magnetic field to generate induced current, there needs to be a speed difference between the rotor conductor and the stator rotating magnetic field. The movement speed of the rotor cannot be completely synchronized with the rotating magnetic field. Therefore AC induction motors are also called asynchronous motors.
Because AC induction motors have a simple structure and do not require the use of permanent magnets, which makes them more economical in some aspects, they are still widely used in many industries.
Advantages of PMSM/BLDC Motors
It can be seen from the structure and working principle that the two types of motors are different. The different structures and principles make the performance bring many differences of the two motors. Compared with AC induction motors, BLDC motors have the following advantages:
- Higher Efficiency: BLDC motors generally have higher efficiency. Induction motors need to generate induced currents and magnetic fields in the rotor during operation. This process has additional losses, while permanent magnet motors do not require excitation current and therefore lose less energy when converting electrical energy into mechanical energy. The overall efficiency of BLDC motors is usually 20~30% higher than that of AC induction motors.

- Higher Power Density:The stator current of the PMSM motor is only used to generate the stator magnetic field, and the permanent magnets will generate the rotor magnetic field. Therefore, under the same size, the permanent magnet motor usually has a higher power density. It can be used in a smaller volume to produces greater power output.
- Faster Response:BLDC motors have faster response and better dynamic performance. They can adjust speed and torque more quickly for applications that require a high degree of control, such as electric vehicles and industrial machinery.
- Operational Stability:AC induction motors may experience speed fluctuations and stalling when the load changes suddenly; while permanent magnet synchronous motors respond faster to speed and torque and operate more stably when the load changes.
- Soft Start:The BLDC motor can be started at low speed by using the driver, the starting current is low, and the impact on the transmission mechanism is also small. The direct starting current of an AC induction motor can reach 5 times the rated current, which has a great impact on the power grid, and the starting speed is high, which can easily cause damage to the transmission structure. Additional soft starter needs to be used to achieve the similar effect of BLDC motor starting.
- Speed Adjustment:The control of the BLDC motor is relatively flexible and convenient. Under the action of the driver, the speed and output power can be adjusted at will, which makes it easier to adjust the motor. AC induction motors require a frequency converter to adjust the speed.
- Precise Control:The control of BLDC motors can be very precise. For example, servo motors and stepper motors can make the rotor rotate at a precise angle or stay at an accurate position. They have more advantages in industrial automation in terms of achieving high efficiency and precise control.
- Lower Maintenance Costs:BLDC motors typically do not require rotor windings and therefore may have lower maintenance costs and longer life.
- Wider Adaptability:BLDC motors have a high efficiency in a wide range of speed and high torque operating ranges. This makes them advantageous in some applications that require high starting torque and low-speed operation, such as electric vehicles or applications that require rapid acceleration.
The Future of BLDC Motor
World industry has crossed over from the era of extensive development. At present and in the future, various industries’ demands for drive solutions and equipment are high efficiency, low energy consumption, high-precision control, lighter, smaller, and high energy density. This will make the demand for BLDC motors very large in the future to meet the requirements of various industries.
Advances in the fields of magnetism and materials science continue to drive the development of permanent magnet materials. The development of new materials improves the performance of permanent magnets and reduces manufacturing costs to a certain extent, making BLDC motors more competitive.
With the continuous advancement of electronic control technology, the ability to accurately control BLDC motors is also improving. Advanced control algorithms and intelligent control systems help optimize motor performance and improve its response speed and efficiency.
The continuous advancement of related technologies are improving the efficiency and performance of BLDC motors, further reduced costs, and enabled them to be applied in more industries.
HF Motion is committed to providing efficient BLDC motors to various industries. Combined with the application scenarios of specific industries, we provide customized motor and controller solutions to make them operate more efficiently, have more comprehensive functions, reduce energy consumption and operating costs.


 HF Motion
HF Motion